This post describes a technique for calculating an adjusted “full extent” for a layer so that content can uniformly fill a map.
The following XAML will display simple map using ESRI’s ArcGIS API for Silverlight. The map contains the world topo map service from ArcGIS Online.
<UserControl
x:Class="ESRI.PrototypeLab.DynamicDesign.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:esri="http://schemas.esri.com/arcgis/client/2009"
mc:Ignorable="d"
d:DesignHeight="600"
d:DesignWidth="800"
>
<Grid Background="Gray">
<esri:Map x:Name="Map">
<esri:Map.Layers>
<esri:ArcGISTiledMapServiceLayer
ID="topo"
Visible="True"
Url="http://services.arcgisonline.com/
ArcGIS/rest/services/World_Topo_Map/MapServer" />
</esri:Map.Layers>
</esri:Map>
</Grid>
</UserControl>
The code behind below will zoom to the full extent of topo map service.
using System.Windows.Controls;
namespace ESRI.PrototypeLab.DynamicDesign {
public partial class MainPage : UserControl {
public MainPage() {
InitializeComponent();
// Zoom to full extent
this.Map.Layers[0].Initialized += (s, e) => {
this.Map.ZoomTo(this.Map.Layers[0].FullExtent);
};
}
}
}
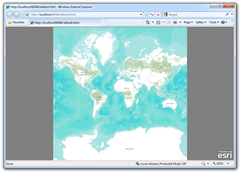
Depending on the aspect ratio of the browser, this will result in a map with “white space” (or whatever color you use for the background) at either the top/bottom or left/right as shown below.
To address this I extended the Layer class with a method to return an adjusted full extent for the parent map.
using System.Windows;
using ESRI.ArcGIS.Client;
using ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Geometry;
namespace ESRI.PrototypeLab.DynamicDesign {
public static class LayerExtension {
public static Envelope AdjustedFullExtent(this Layer layer,
FrameworkElement parent) {
Envelope extent = layer.FullExtent;
double ratioMap = parent.ActualHeight / parent.ActualWidth;
double ratioLay = extent.Height / extent.Width;
if (ratioMap < ratioLay) {
return new Envelope() {
XMin = extent.XMin,
YMin = extent.GetCenter().Y - 0.5d * ratioMap *
extent.Width,
XMax = extent.XMax,
YMax = extent.GetCenter().Y + 0.5d * ratioMap *
extent.Width
};
}
return new Envelope() {
XMin = extent.GetCenter().X - 0.5d *
extent.Height / ratioMap,
YMin = extent.YMin,
XMax = extent.GetCenter().X + 0.5d *
extent.Height / ratioMap,
YMax = extent.YMax
};
}
}
}
Let’s modify the code behind to use the new method, AdjustedFullExtent, defined above.
using System.Windows.Controls;
namespace ESRI.PrototypeLab.DynamicDesign {
public partial class MainPage : UserControl {
public MainPage() {
InitializeComponent();
// Zoom to full extent
this.Map.Layers[0].Initialized += (s, e) => {
this.Map.ZoomTo(
this.Map.Layers[0].AdjustedFullExtent(this.Map));
};
}
}
}
Now, when the application starts, the layer will fill the entire map regardless of the browsers aspect ratio.