A common obstruction when developing Silverlight web applications is cross domain access. Silverlight has built-in security that prevents communication to servers that do not explicitly granted access using with either a client access policy or cross domain file. Even though a server has services intended for public use, if the server does not have a cross domain file then Silverlight apps will be denied access.
This post presents a convenient and legitimate way to overcome this restriction with a simple proxy service in three easy steps!
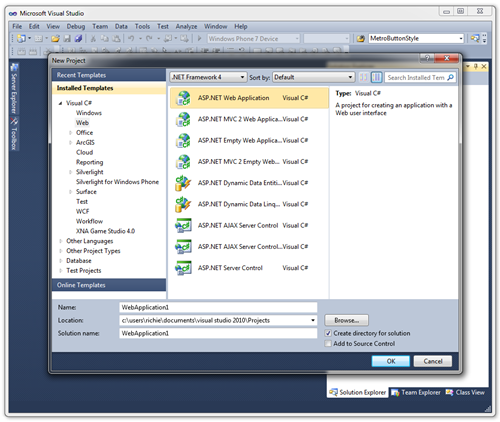
Step 1 – In Visual Studio 2010, create a new ASP.NET Web Application project called WebApplication1
Step 2 – Add a new generic handler called proxy.ashx
Step 3 – Copy and paste this code into proxy.ashx.cs.
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Web;
namespace WebApplication1 {
public class proxy : IHttpHandler {
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context) {
HttpResponse response = context.Response;
// Check for query string
string uri = Uri.UnescapeDataString(context.Request.QueryString.ToString());
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(uri)) {
response.StatusCode = 403;
response.End();
return;
}
// Filter requests
if (!uri.ToLowerInvariant().Contains("wikimedia.org")) {
response.StatusCode = 403;
response.End();
return;
}
// Create web request
WebRequest webRequest = WebRequest.Create(new Uri(uri));
webRequest.Method = context.Request.HttpMethod;
// Send the request to the server
WebResponse serverResponse = null;
try {
serverResponse = webRequest.GetResponse();
}
catch (WebException webExc) {
response.StatusCode = 500;
response.StatusDescription = webExc.Status.ToString();
response.Write(webExc.Response);
response.End();
return;
}
// Exit if invalid response
if (serverResponse == null) {
response.End();
return;
}
// Configure reponse
response.ContentType = serverResponse.ContentType;
Stream stream = serverResponse.GetResponseStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[32768];
int read = 0;
int chunk;
while ((chunk = stream.Read(buffer, read, buffer.Length - read)) > 0) {
read += chunk;
if (read != buffer.Length) { continue; }
int nextByte = stream.ReadByte();
if (nextByte == -1) { break; }
// Resize the buffer
byte[] newBuffer = new byte[buffer.Length * 2];
Array.Copy(buffer, newBuffer, buffer.Length);
newBuffer[read] = (byte)nextByte;
buffer = newBuffer;
read++;
}
// Buffer is now too big. Shrink it.
byte[] ret = new byte[read];
Array.Copy(buffer, ret, read);
response.OutputStream.Write(ret, 0, ret.Length);
serverResponse.Close();
stream.Close();
response.End();
}
public bool IsReusable {
get { return false; }
}
}
}
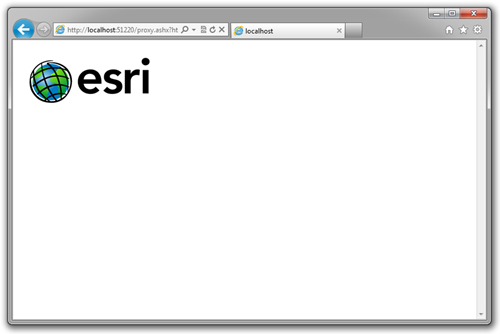
You are done! To test, press F5 to run the web application in debug mode. Your default web browser will display the Default.aspx page from your project.
Without closing the web browser, append the name of the proxy service and the web resource (highlighted below) that you need access to. For example:
http://localhost:51220/proxy.ashx?http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/f/f0/New-esri-logo.jpg
This is the result.
In summary, this post described how to crate a simple proxy web service. The proxy can be used by Silverlight web application to access resources that are restricted due to a missing cross domain file. To prevent malicious use of the proxy it is advisable to add some sort of access restriction, for example, in this exercise the proxy was configured to only accept requests for content from the wikimedia.org domain.


hi,
ReplyDeletethanks for code.
how can i send post data to a page on this proxy service.
the solution is that :
ReplyDeleteStream newStream = webRequest.GetRequestStream();
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(HttpContext.Current.Request.InputStream);
byte[] bytes = sr.CurrentEncoding.GetBytes(sr.ReadToEnd());
newStream.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
newStream.Close();
sr.Close();
webRequest.ContentType = "text/xml";
@trda. Thanks for the clarification.
ReplyDeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteThank you for a highly interesting plog post. I read the question of trda ”How can i send post data to a page on this proxy service.” and your answer. However I cannot interpret your answer and I have some questions I would be most happy if you please could answer:
(1) What does the new code allow the proxy to do?
(2) Were in your original published code goes the modification?
(3) In my application the proxy shall add (optimal) post data. Is that what the code in the Answer does?
(4) If not, how can this (3) be accomplished?
(5) Are there any special (know) limitation what calls cannot be made throw the proxy? What about https?
Most grateful for answers to these questions,
Ulf L
PS. Sorry, I meant to write “optional” and “known”.
ReplyDelete